Nausea and vomit are common signs and symptoms that may be caused by various conditions. Nausea and vomit are usually because of microorganisms inflammatory disease — often erroneously known as gastroenteritis — or the sickness of early pregnancy. Nausea is an uneasiness of the abdomen that always comes before vomit. Vomiting is that the forceful voluntary or involuntary evacuation (“throwing up”) of abdomen contents through the mouth.
Many medications will cause nausea and vomit, as can general anesthesia for surgery. Rarely, nausea and vomit might indicate a heavy or perhaps grave drawback.
How bulimia affects the human body
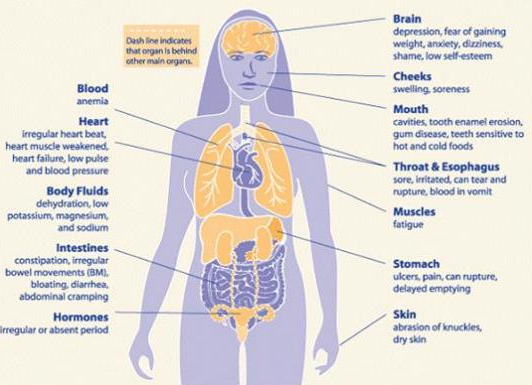
Causes
Nausea and vomiting may occur separately or together. Common causes include:
-Chemotherapy
-Gastroparesis (a condition within which the muscles of the abdomen wall do not operate -properly, interfering with digestion)
-General anesthesia
-Intestinal obstruction
-Migraine
-Morning sickness
-Motion sickness: First aid
-Rotavirus
-Vestibular neuritis
-Viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu)
Other possible causes of nausea and vomiting include:
-Acute liver failure
-Alcohol use disorder
-Anorexia nervosa
-Appendicitis
-Brain tumor
-Bulimia nervosa
-Crohn’s disease
-Cyclic vomiting syndrome
-Depression (major depressive disorder)
-Diabetic ketoacidosis
-Dizziness
-Ear infection (middle ear)
-Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
-Fever
-Food poisoning
-Gallstones
-Generalized anxiety disorder
-Heart attack
-Heart failure
-Hepatitis
-Hydrocephalus
-Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
-Hypoparathyroidism (underactive parathyroid)
-Intestinal ischemia
-Intestinal obstruction
-Intussusception (in children)
-Irritable bowel syndrome
-Medications (including aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, oral contraceptives, digitalis, narcotics and antibiotics)
-Meningitis
-Milk allergy
-Pancreatic cancer
-Pancreatitis
-Peptic ulcer
-Pyloric stenosis (in infants)
-Radiation therapy
-Severe pain
-Toxin ingestion
The causes of vomiting differ according to age. For youngsters, it is common for vomiting to happen from a viral infection, poisoning of food, milk allergy, motion sickness, overeating, coughing, or blocked intestines and in other cases illnesses in which the child is running on a high fever.
The temporal order of the nausea or vomit will indicate the cause. When appearing shortly once a meal, nausea or vomiting may be caused by food poisoning, gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining), an ulcer, or bulimia. Nausea or vomit one to eight hours after a meal may additionally indicate unwellness. However, certain food- borne bacterium, like enteric bacteria, will take longer to provide symptoms.
Take it seriously if nausea and vomiting are accompanied by other warning signs, such as:
-Chest pain
-Severe abdominal pain or cramping
-Blurred vision
-Confusion
-High fever and stiff neck
Treatment regardless of any age includes:
-Drinking gradually larger amounts of clear liquids.
-Avoiding solid food until the vomit episode has passed.
-If vomiting and diarrhea last more than 24 hours, an oral rehydrating solution such as Pedialyte should be used to prevent and treat dehydration.