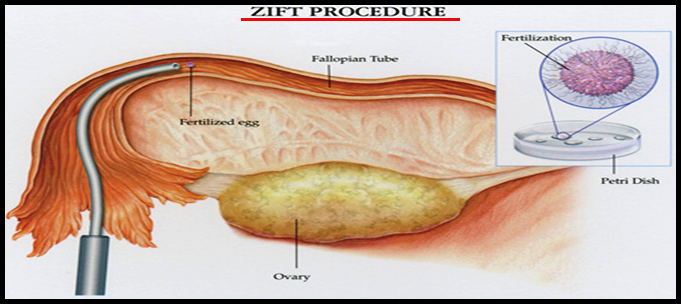
ZIFT is an assisted reproductive technology, that is similar to the in vitro fertilization technology and the transfer of the embryo, but the difference is that in this technique the embryo is transferred to the fallopian tube. Due to the transfer of the fertilized eggs, directly into the tubes, this process is also known as the tubal embryo transfer (TET). As compare to the gamete intrafallopian transfer, this process is more successful, because there are greater chances of ensuring the fertilization of the eggs. For ZIFT technology to work, the women must have healthy tubes.
ZIFT is a good idea for those women who cannot get pregnant with the normal in vitro fertilization. This process is closer to natural conception. It takes 5-6 weeks to complete the ZIFT cycle. After the stimulation of egg production, the growth of ovarian follicles will be monitored by the doctor, and as they get mature an injection will be given to the women, containing human chorionic gonadotropins.
How ZIFT is performed?
It is an assisted reproductive procedure, and it involves the few steps which are stated below.
- The ovaries of women are stimulated with the medication, for increasing the probability of producing multiple eggs.
- The aspiration procedure is used for the collection of eggs.
- In the laboratory, the fertilization is done in the same way as for IVF. But there is the exception of the time frame. In this procedure, the transfer of fertilized eggs is done within 24 hours.
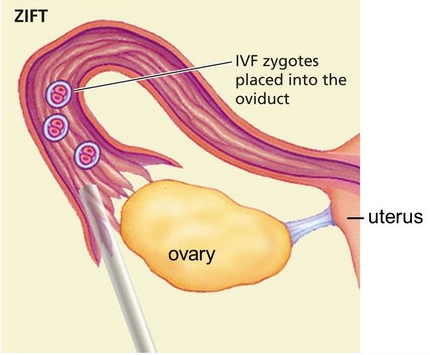
- Then, a laparoscopic procedure is used, for the transfer of fertilized eggs. The deep placing of the catheter is done into the fallopian tubes, and the fertilized egg is injected.
- In the final step, the early pregnancy symptoms are observed. Blood tests will be used by fertility specialists, for the determination of pregnancy.
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
When ZIFT is used
It is used for infertility situations, where at least one fallopian tube can function normally, and all other treatments have been failed to help conception. Normally, it is used when there is a blockage in the fallopian tube, and due to this blockage, the normal binding of sperms to the eggs is not possible by the natural means. In all cases, it has a success rate of about 64.8%. It is an assisted reproductive technology, and it can be used for many infertility related issues except for the tubal blockage, significant tubal damage, sperm that cannot penetrate to the egg, and the anatomic problems of the uterus, such as for the severe intrauterine adhesions.